
The most common type of manganese is manganese (II) oxide (MnO), which is predominant in nature. This form of manganese is crucial because it acts as a key ore of the metal and is …
Learn more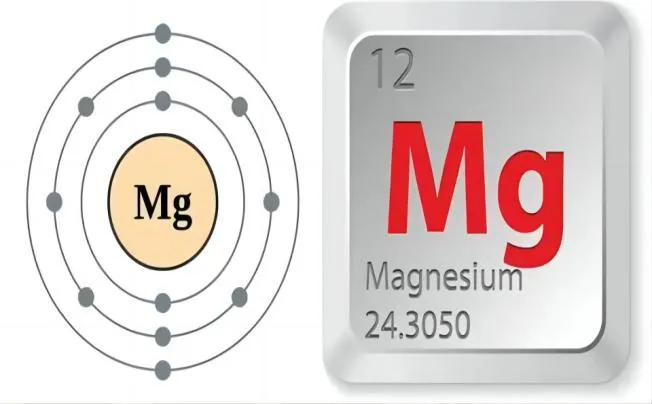
One mineral that is necessary for many different body processes is magnesium. It is essential for supporting over 300 enzymes that carry out different chemical reactions in the bod…
Learn more
Magnesium is an atomic number twelve element represented by the symbol Mg. It is a low density, low melting point, and highly reactive metal that has a glossy grey colour. It only …
Learn more
Magnesium is an atomic number twelve element represented by the symbol Mg. It is a low-density, low melting point, and highly reactive metal that has a glossy grey colour. It only …
Learn more
Flux core wire is a type of welding electrode that consists of a metal sheath surrounding a core filled with flux materials. The flux compounds are designed to release shielding ga…
Learn more
Aluminum and magnesium, two elemental treasures of the periodic table, have captivated the realms of science, engineering, and industry with their remarkable properties. Aluminum, …
Learn more
Flux core welding, a popular arc welding process, employs a tubular wire electrode with flux material inside. This unique design eliminates the need for an external shielding gas, …
Learn more
Welding has long been an essential technique in metal fabrication, allowing for the fusion of materials to create durable structures. Among the various welding methods available, f…
Learn more
Mig welding wire, also known as solid wire electrode, is a type of welding consumable used in the Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) process. It is typically made of a solid, bare metal …
Learn more
Flux core wire, also known as flux-cored arc welding (FCAW) wire, is a type of welding consumable that contains flux within its core. This flux serves multiple purposes during the …
Learn more