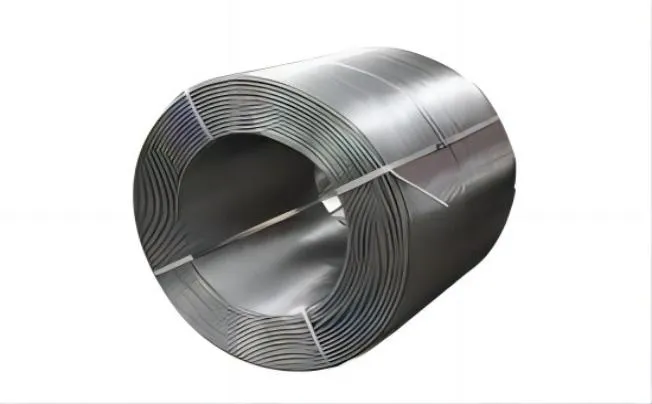

Cored wire, a consumable tubular electrode with a metallic sheath filled with various powders or alloys, plays a crucial role in modern welding applications. Its primary function i…
Learn more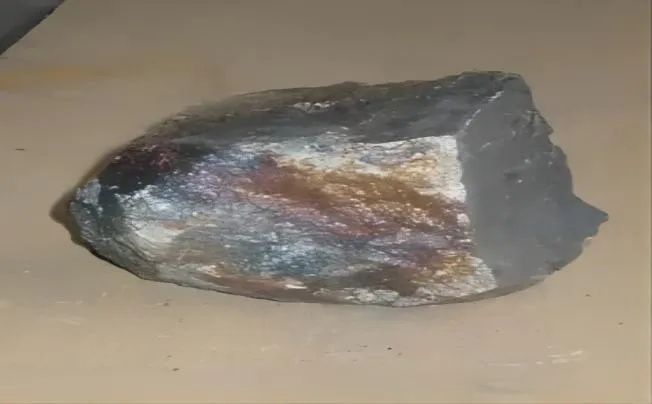
In its simplest form, ferrotitanium is an alloy composed primarily of iron and titanium. The proportion of each element can vary depending on the desired characteristics of the fin…
Learn more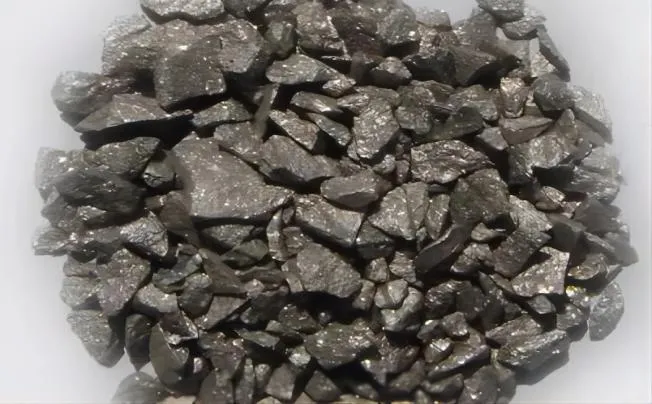
Ferrotitanium, a crucial alloy in the realm of metallurgy, is a composite material primarily composed of iron and titanium. This alloy is known for its exceptional strength-to-weig…
Learn more
Metal powder, or a combination of metal and non-metal powder, is the raw material used in the powder metallurgy process. It is then molded and sintered to create metal materials, c…
Learn more
Ferrotungsten, a fascinating alloy composed primarily of iron and tungsten, stands as a testament to human ingenuity in metallurgy. This alloy is predominantly used in the manufact…
Learn more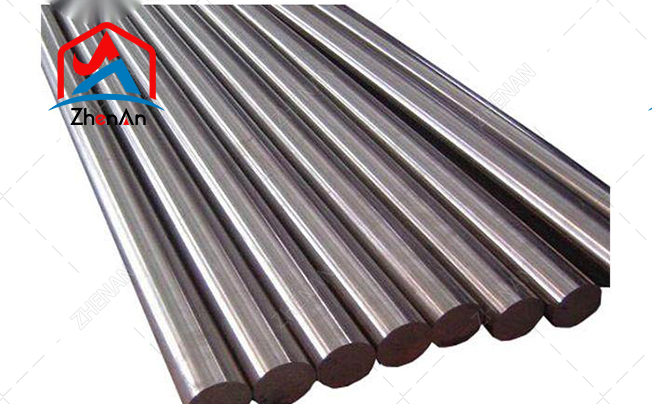
Nickel tube is a rod-shaped object made of nickel. It is a raw material for processing. Nickel is a silver-white metal with a density of 8.9 g/cm3.
Learn more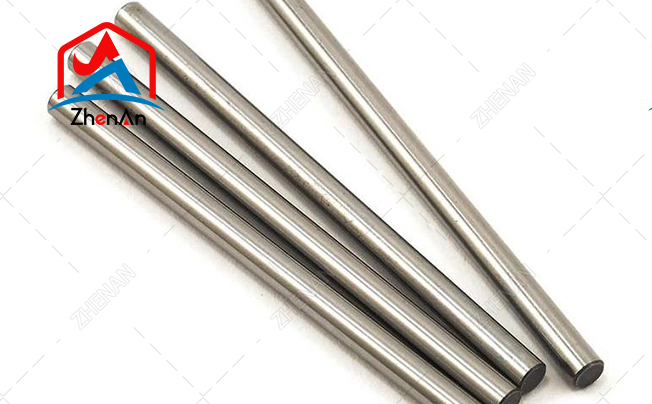
Hastelloy is a nickel-based corrosion-resistant alloy, mainly divided into two categories: nickel-chromium alloy and nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy. Hastelloy has good corrosion …
Learn more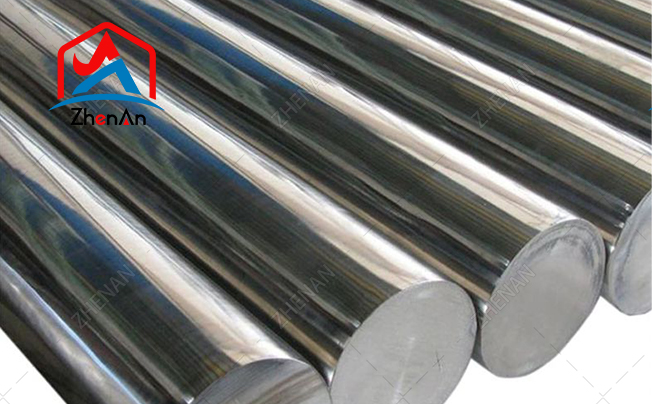
Nickel is a slightly yellowish silver-white metal that is hard, easy to polish, magnetic (not as good as iron and cobalt) and has good plasticity.
Learn more
Nickel is the 23rd most abundant element in the earth's crust.
Learn more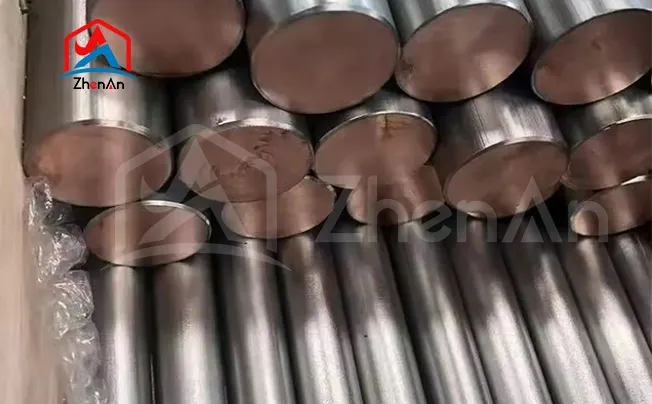
Titanium-copper composite rod, also known as titanium-clad copper, is a copper rod covered with a titanium layer of a certain thickness and is the main component of the metal anode…
Learn more